Journal article on ultrafast control of excitons in 2D semiconductors using optical coherence phenomena
Pubished work of our division in a high-ranked journal about the control of particle (electron-hole pair) polarization in 2D materials of the type WSe2 and MoS2.
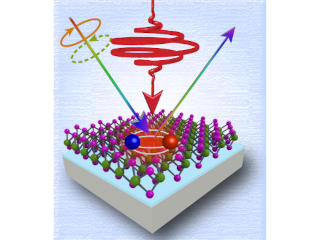
A team of researchers led by Martin Kozák from KCHFO published an article about the manipulation of exciton energy levels in WSe2 and MoS2 monolayers. Paper was published in in the journal npj 2D Materials and Applications. In this work, the researchers demonstrated that irradiation of monolayers of transition metal dichalcogenides with strong circularly polarized infrared laser pulses can lift the energy degeneracy of exciton states in these materials. Excitons are quasiparticles that consist of an electron and a hole bound by the Coulomb interaction. The energy of these quasiparticles generally depends on their wave vector. In some semiconductors, including the materials investigated in this work, there are several energy degenerate minima in the exciton dispersion relations. These form so-called valleys that can be occupied by excitons. Application of circularly polarized ultrashort infrared pulses blue-shifts individual valleys (shift to higher energies), and this shift differs for the two classes of non-equivalent valleys when circularly polarized light is applied. These findings open the door to the ultrafast control of valley polarization of carriers in 2D materials for valleytronics operating at multiterahertz frequencies.